
Sup252
CT Image Storage for Processing
This Supplement adds For Processing storage SOP Classes based on the
existing CT Image IOD, Enhanced CT Image IOD, and Legacy Converted
Enhanced CT Image IOD.
For Processing storage SOP Classes in DICOM facilitate the exchange
and storage of images needed for processing while distinguishing them
from those for presentation.
This supports appropriate data pipelines while not disrupting reading
workflow with images not intended for presentation.
These new SOP Classes mirror existing Mammography, Intra-Oral X-ray,
and Digital X-ray For Processing SOP Classes.
One application of the For Processing SOP Classes is to store and
exchange CT basis images created by the multi-energy decomposition
process.
These are not typically diagnostic themselves, but can be processed to
generate an extensive variety of diagnostic images (iodine maps,
virtual non-contrast images, virtual monoenergetic images at various
energy levels, calcium maps, etc.).
Hanging Protocols would typically ignore these For Processing
images.
This supplement will be further presented and
discussed in the base standard group before going
out for Letter Ballot.
View slideset »

Sup245
RDSR Informative Annex
This Supplement explains the creation and usage of
Radiation Dose Structured Report (traditional and
enhanced) within Angiography, Mammography, Radiography,
Radiofluoroscopy, CT, and Dentistry modalities.
This supplement excludes Radiopharmaceutical Radiation
Dose Structured Report, Patient Radiation Dose Structured
Report, and radiation for treatment (which is encoded in
the family of Radiotherapy objects).
The content definition of the RDSR varies by modality, and
there are many different types of system configurations in
the field.
This supplement provides a clear understanding of the
precise requirements for each type of device.
The purpose of this supplement can be summarized as
follows:
- Give more information beyond the definitions in PS 3.16: describe real-world scenarios of typical equipment configurations, provide examples and encoding guidelines;
- Indicate restrictions on the applicable scenarios (defined terms, value ranges, presence of Content Items);
- Assess the applicability for some conditional Content Items under particular scenarios;
- Promote usage of optional Content Items under particular scenarios;
- Explain similarities and equivalences of same
information in both traditional RDSR and enhanced RDSR.
<\ul>
Encoding examples of using the traditional RDSR and the
enhanced RDSR (introduced in Supplement 214), and mapping
between these two RDSRs.
The work of this Supplement was undertaken in liaison with the America Association of Physicists in Medicine (AAPM) and European Federation of Medical Physicists (EFOMP).
This supplement was voted ready to go out for Public Comment.
View details »
View slideset »
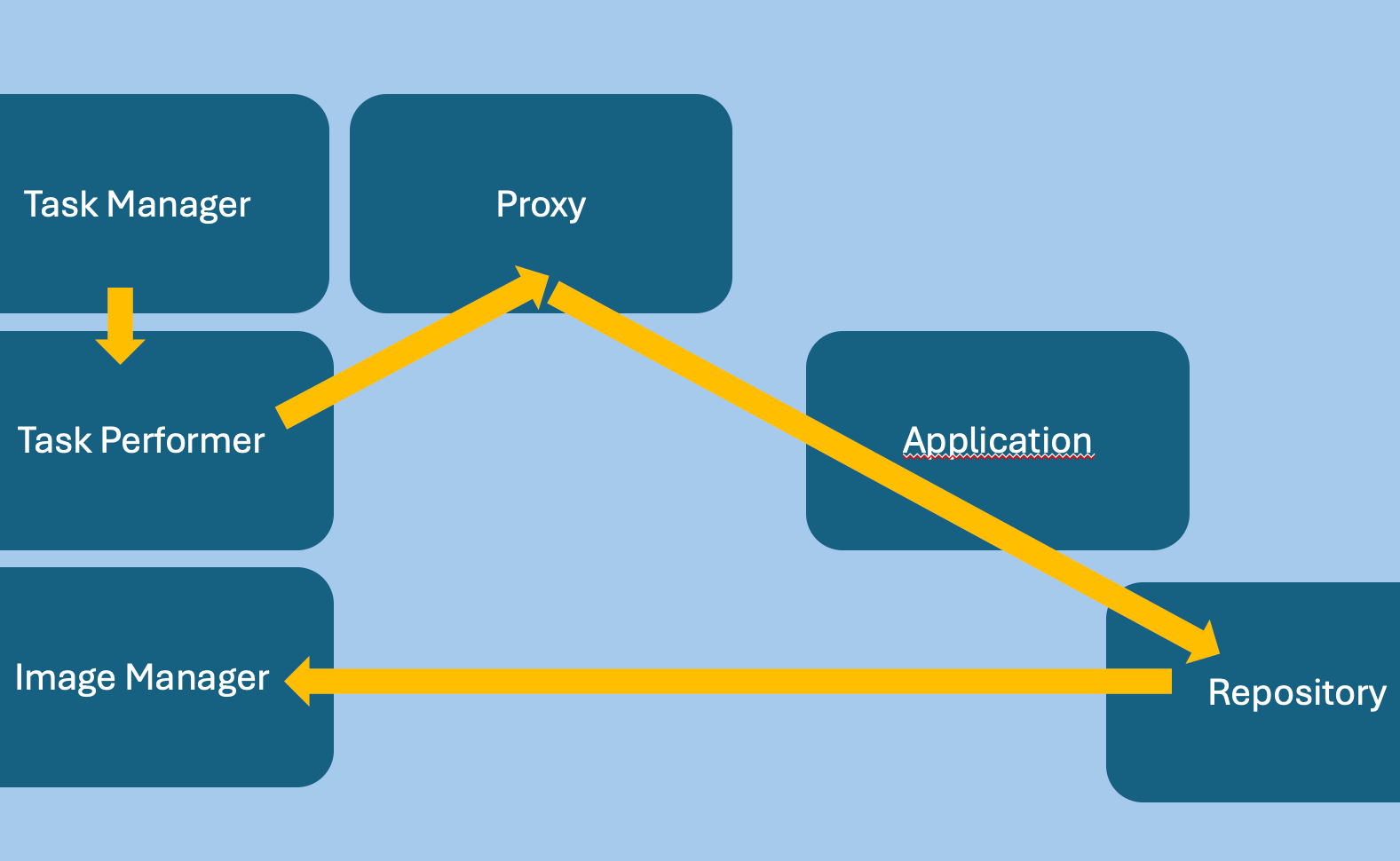
Sup251
Application Request
This Supplement adds an Application Processing Request Service to
DICOM PS3.18.
This service allows a user agent (client) to request an origin server
(Application) to perform work.
The request identifies initial data to be used as well as the
protocols which can be used to retrieve the data.
The request also specifies the protocol to be used upon completion to
store resulting artifacts.
This service is partially based on an API proposed by the American
College of Radiology’s Data Science Institute (ACR DSI) that was
extended by the MONAI Deploy Informatics Gateway (MIG) for inference
requests.
Although this service might be used to perform work identified in a
DICOM UPS-RS workitem, the interaction of this service with the
Worklist Service is not specifically defined.
This supplement will be further presented and discussed in the base
standard group before going out for Public Comments.
View slideset »

Sup250
2D Total Body Photography
This supplement introduces 2D Total Body Photography (TBP) Regional Image
Information Object Definition (IOD) for imaging of a skin region.
Total Body Photography (TBP) aims to image a person’s entire skin
surface.
TBP is predominantly used for sequential screening for skin cancer, in
particular melanoma, but can also be used for the assessment of
inflammatory skin diseases such as psoriasis.
TBP may be 2D or 3D. This supplement addresses 2D TBP. 2D TBP produces 2D planar images,
whereas 3D TBP produces volumetric images.
TBP uses visible light imaging. Camera movement may be manual or
automatic.
Image acquisition typically occurs with the patient in multiple
positions. Multiple regional images are acquired to image entire skin
surface. TBP is often used in combination with dermoscopy.
This supplement will be further presented and discussed in
the base standard group before going out for Public
Comments.
View slideset »

Sup248
DICOMWeb Send
This supplement adds Send Transactions to DICOMweb’s
Studies and Non-Patient Instances Services to mirror the
C-MOVE operation that is already available in DIMSE.
The Send Transactions have been de- signed with the
intention of facilitating proxies from/to DIMSE.
This supplement will be further presented and
discussed in the base standard group before going
out for Public Comments.
View slideset »